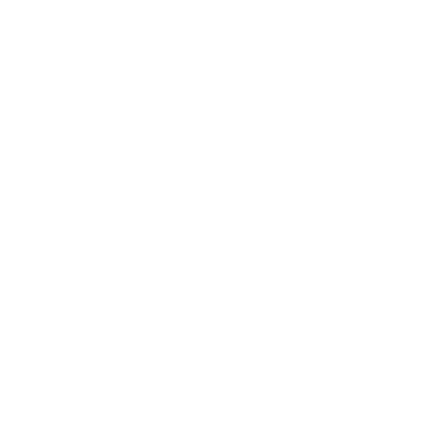
“Steel has been an essential part of human progress for centuries.“
Steel has been the backbone of industrial progress for centuries, but in 2024, it continues to prove its importance in new and exciting ways. As industries evolve, so too does steel, with advancements that have not only made it more versatile and stronger but also greener and more innovative. The developments surrounding steel in 2024 are a testament to human ingenuity and our constant pursuit of better, more sustainable materials. Here are the top 10 amazing facts about steel in 2024 that show just how integral this material is to modern life.
Fact One: Ultra-High-Strength Steel is Now a Reality
One of the most groundbreaking developments in 2024 is the increased use of Ultra-High-Strength Steel (UHSS). This remarkable material represents a significant leap forward in the evolution of steel technology. Engineered to combine extraordinary strength with a lighter weight, UHSS has opened up new possibilities across several industries that rely on durable and resilient materials. Its impressive strength-to-weight ratio means that UHSS can withstand high levels of stress and strain without increasing the overall weight of the structure or product—making it ideal for applications where both safety and efficiency are paramount.

Fact Two: Steel is Leading the Way in Carbon Neutrality
In 2024, the steel industry is at the forefront of the global push toward carbon neutrality, with a transformative commitment to reducing its environmental impact and making steel a sustainable choice for the future. Traditionally, steel production has been an energy-intensive process, heavily reliant on fossil fuels that release large quantities of carbon dioxide (CO₂) into the atmosphere. However, with the growing urgency of climate change and the pressing need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, leading steel manufacturers are adopting innovative, environmentally conscious practices to produce what is now referred to as “green steel.”

Fact Three: Self-Healing Steel is Now Commercially Available
In what feels like a leap straight from the pages of a science fiction novel, the advent of self-healing steel has become a reality, and it’s now commercially available. This remarkable material possesses the groundbreaking ability to autonomously repair small cracks and damages, significantly enhancing the durability of steel structures. Such a development is particularly revolutionary for critical infrastructure and high-stress applications, where it not only extends the lifespan of steel components but also slashes maintenance costs and downtime. This innovation marks a transformative step in materials engineering, promising a future where steel structures are more resilient and sustainable than ever before.

Fact Four: Smart Steel Bridges for Smart Cities
As smart cities continue to expand and evolve, the demand for infrastructure that aligns with advanced technology has grown significantly. In response, steel bridges equipped with cutting-edge sensors are now being constructed across the globe. These innovative “smart bridges” are designed to monitor critical factors such as metal strain, steel temperature, and corrosion levels continuously. By collecting and analyzing this data, the sensors provide real-time alerts to maintenance teams, allowing them to address potential issues promptly and proactively. Enhancing safety of the bridges and extending their lifespan.

Fact Five: Steel in Modular and Prefabricated Construction
The use of steel in modular and prefabricated construction is experiencing unprecedented growth, rapidly reshaping the landscape of the building industry. In 2024 alone, it’s projected that an impressive 30% of all new buildings worldwide will be constructed using pre-engineered steel modules. This shift marks a major advancement in construction practices, significantly reducing building times and minimizing material waste. Furthermore, these modular steel solutions contribute to a smaller environmental footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals. Steel’s role continues to expand, paving the way for a sustainable future.

Fact Six: Steel is Key to Renewable Energy Storage
Steel has firmly established itself as a fundamental component in renewable energy storage solutions, playing an essential role in supporting the global shift towards sustainable energy sources. Large-scale energy storage facilities, particularly those utilizing advanced vanadium flow batteries, are now emerging as highly efficient systems for storing and distributing renewable energy across power grids. These batteries, which depend on the strength, durability, and stability that only steel can provide, enable secure containment and long-term functionality, ensuring that renewable energy can be reliably stored and dispatched as needed. As the demand for green energy grows, steel’s role is indispensable.

Fact Seven: Nanotechnology & Steel Structures
Nanotechnology holds tremendous promise for advancing the construction industry. By integrating nanotechnology into traditional building materials like concrete, steel, glass, coatings, and wood, we can significantly enhance their performance and durability. This innovation not only lowers production and maintenance costs but also paves the way for more sustainable construction practices, making it a key driver in building the efficient, eco-friendly structures of the future. Nanotechnology & steel come closer together in the future of construction. Nanotechnology aims to manufacture these nanomaterials and engineer them to build enhanced systems for economical, sustainable and efficient applications.
Fact Eight: Recycled Steel is at an All-Time High
The global demand for recycled steel has been rising at an unprecedented rate. In 2024 alone, approximately 80% of all newly produced steel products are crafted from recycled materials. This remarkable shift has been driven by major advancements in recycling technology, enabling the industry to process and repurpose steel more efficiently than ever before. Coupled with an unwavering commitment to sustainability, the steel industry is actively reducing its environmental footprint, conserving natural resources, and cutting down on energy use and emissions. This transformation underscores a broader movement toward a circular economy, where steel’s inherent recyclability is leveraged to create a cleaner, greener future.
Fact Nine: Steel in Next-Gen Public Transport
Steel plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of public transport, offering unparalleled durability, sustainability, and safety to support expanding infrastructure. As cities worldwide embrace eco-friendly initiatives and strive to reduce carbon footprints, steel remains a top choice due to its recyclability and long lifecycle. Innovations in steel production, such as high-strength, corrosion-resistant, and wear-resistant grades, are meeting the evolving demands of modern transport systems, making them more efficient and resilient. By investing in steel-based public transport infrastructure, we pave the way for sustainable urban growth and reliable transit solutions that can meet the needs of future generations.

Fact Ten: Stainless Steel’s Role in Space Exploration
In 2024, stainless steel has become a cornerstone of space exploration, playing a vital role in everything from the construction of rocket launch pads to the intricate components of space stations orbiting our planet. Engineers and scientists are pushing the boundaries by testing new stainless steel alloys specifically designed to withstand the extreme environments of outer space. These advanced materials promise enhanced durability, strength, and resilience, paving the way for safer and more efficient space missions. With each innovation, stainless steel continues to drive progress in the exploration of the final frontier, ensuring that spacecraft and structures are equipped to meet the challenges of space like never before.

Contact Us To Find Out More
We ensure a fast, exact and economical steel solution for our clients. Call our team today to discuss your steel cutting and metal processing requirements.
Get Our Newsletter
Contact details
121 Mica Street, Carole Park,
QLD, 4300, AUSTRALIA
Freecall: 1800 SHAPECUT (1800 742 732)
Telephone: (07) 3271 5600
Facsimile: (07) 3271 5454
Email: sales@shapecut.com.au
Accredited Profile Cutting

Profile Cutting
Metal Processing Services
©2025 ShapeCut | Website design Brisbane by iFactory | Privacy Policy | Search | Sitemap



